
Table of Contents
Standard Recreational Vehicle: Certification, Laws and Regulations are complex federal, state, and local compliance requirements for vehicle certification. RV certification requirements mandate specific safety standards enforced by Department of Transportation (USDOT) regulations. Manufacturers must meet strict federal motor vehicle safety standards before standard recreational vehicle production.
Vehicle classifications determine legal weight, size, and operational restrictions. RV owners must register vehicles according to specific state transportation guidelines. RV rules and regulations govern parking, overnight stays, and operational constraints across multiple States.
RV park regulations define specific zoning laws for temporary and permanent vehicle placement. Insurance mandates require comprehensive coverage matching vehicle classification, and safety inspections validate vehicle roadworthiness through periodic mechanical examinations.
Legal considerations address full-time living modifications and compliance with local residential codes. Penalties include fines, vehicle impoundment, and potential registration revocation for non-compliant recreational vehicles.
What are the RV Standards?
The RV Standards are listed below.
- Safety Requirements: Safety requirements are rules set to protect owners using RVs. The rules cover fire safety, electrical systems, and structural strength.
- Insurance: Insurance is a contract that protects RV owners from financial loss. It covers damages from accidents, theft, or natural disasters. Insurance is essential in the RV industry to avoid high costs from unexpected events.
- Size and Weight Limits: Size and weight limits are laws that set how big and heavy an RV is. The weight limits ensure RVs are safe to drive and do not damage roads.
- Speed Limits: Speed limits are the maximum speeds allowed for RVs on different roads. The speed limits are set to keep drivers safe and reduce accidents. Follow speed limits to avoid penalties and ensure safety.
- Towing Regulations: Towing regulations are rules about how RVs tow other vehicles or trailers. The regulations and rules cover hitching, lighting, and braking systems. Following towing regulations ensures safe travel and prevents accidents.
- Seatbelt Laws: Seatbelt laws require drivers in an RV to wear a seatbelt while driving. The laws are in place to protect passengers in case of an accident. Not wearing a seatbelt leads to fines and increased injury risk.
- Licensing and Registration: Licensing and registration are legal requirements for RVs. Licensing ensures drivers are qualified, and registration makes driving the RV legal.
- Parking and Overnight Stays: Parking and overnight stay regulations control where RVs park and sleep. Overnight stays vary by location and help manage traffic and safety. RV owners must follow the regulations to avoid fines and respect local laws.
- Waste Disposal: Waste disposal regulations set how to handle and dispose of waste from RVs. Proper disposal prevents pollution and protects the environment.
- Propane Transport: Propane transport regulations govern how to carry and store propane in RVs safely. Propane Transport prevents accidents and ensures safety.
- Zoning and Land Use: Zoning and land use regulations control where RVs are parked or used. Local governments set land use to manage land use.
- Emissions Standards: Emissions standards limit the amount of pollution RVs produce. The standards help protect air quality and the environment. Complying with emissions standards is required for legal operation.
- Age Restrictions: Age restrictions set the minimum age of 32 to 53 for driving or owning an RV. Restrictions ensure RV owners have the maturity and skills needed for safe operation.
- International Travel: International travel regulations set the rules for taking RVs across country borders. International travel covers things like customs, insurance, and vehicle requirements.

What Federal Standards Govern RVs?
Federal standards govern RVs through regulations enforced by government agencies overseeing manufacturing, safety, and environmental compliance. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) enforces Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) for recreational vehicles, which require specific features such as brakes, lighting, and occupant protection.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets emissions limits for RV generators and engines to reduce air pollution. RV manufacturers must install USDOT-approved safety glass windows and emergency exits in standard recreational vehicles. The FMVSS mandates installing smoke detectors and carbon monoxide alarms in living spaces. RV electrical systems require certification under the National Electric Code (NEC) guidelines for appliance connections and wiring.
Each manufacturer submits compliance reports to federal agencies to track vehicle identification numbers (VIN) through federal databases. The government demands proper labeling to display vehicle weight ratings and tire specifications. Purchasing an RV Extended Warranty helps owners maintain compliance with federal safety standards throughout ownership.
How do State RV Laws Differ?
State RV Laws differ through specific regulations governing vehicle length, width, and height restrictions across jurisdictions. RV laws by state establish maximum lengths of 45 feet in California, while Florida permits 50-foot recreational vehicles. Height limits vary from 13.6 feet in northeastern states to 14 feet in western regions. States set width restrictions at 8.5 feet for travel safety.
Federal guidelines require RVs under 26,000 pounds to operate without commercial licensing. Road access rules designate RV routes along major highways and state roads. Parking limits range from 24 hours in urban areas to 14 days in rural locations.
Different regulations affect RV operation and ownership. Texas requires annual safety inspections, while Arizona mandates testing every two years. California enforces emission standards for motorized RVs made after 1998, while Florida exempts RVs from property taxes but charges registration fees based on weight.
Colorado bans overnight RV parking above 11,000 feet, while Nevada allows RV parking at casinos without time limits. Washington requires carbon monoxide detectors in all RVs, and Oregon mandates special licensing for RVs over 40 feet. Idaho permits triple towing under specific conditions. Utah designates RV-only camping areas in state parks with extended stays.

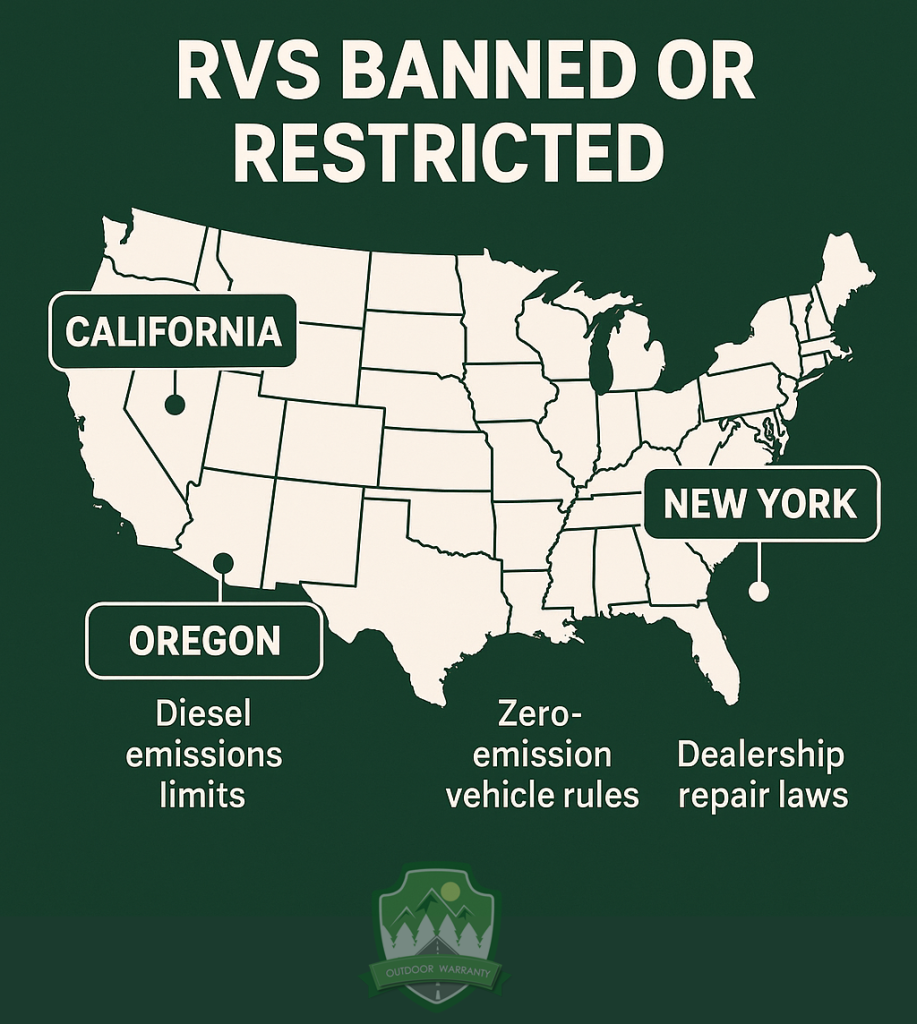
Which States were RVs Banned?
The states were RVs are banned or restricted include California, Oregon, and New York. California has proposed strict air quality regulations limiting diesel-powered RV emissions, restricting older RVs from operating in California. The restrictions are part of efforts by the Air Resources Board to meet California’s goals for reducing air pollution and encouraging zero-emission vehicles.
The Environmental Quality Commission in Oregon has implemented rules requiring medium- and heavy-duty vehicle manufacturers, including RV manufacturers, to sell zero-emission vehicles as a certain percentage of new vehicle sales, starting in 2025 and increasing to 100% by 2036. The regulations have faced opposition from the RV industry due to concerns about technological advancements and infrastructure support.
The Attorney General in New York secured $50,000 for RV owners who do not obtain timely repairs, addressing issues related to RV dealership practices. Consumer protection measures aim to ensure RV owners are not unfairly impacted by delayed service or unfulfilled warranties.
The conditions impact the ownership experience, even without a direct ban, as New York residents face longer repair wait times and potential service issues. New York law requires RV dealerships to adhere to repair timelines, offering a legal route for owners to address offenses.
Where can You Legally Park an RV Overnight?
You can legally park an RV overnight in designated areas such as RV parks, campgrounds, and retail parking lots that permit overnight stays. RV parks and campgrounds offer amenities like hookups and waste disposal, making RVs suitable for overnight stays. Retailers like Walmart and Cracker Barrel allow overnight parking, but RV owners check with the store manager and adhere to local ordinances.
Always obtain permission before parking overnight in any location to ensure compliance with local laws and regulations. RV owners must follow the specific RV park rules and RV park regulations set by the facility when staying overnight in an RV park or campground. The rules include guidelines on noise levels, pet policies, check-in and check-out times, and waste disposal procedures.
Adhering to the regulations ensures a pleasant experience for all drivers and helps maintain the park’s standards. Review the park’s rules and regulations to ensure compliance and avoid issues before making a reservation.

Is RV Certification Required?
Yes, RV certification is required for standards to ensure safety, quality, and compliance with industry regulations. RV certification is a process that confirms an RV meets the required safety, manufacturing, and environmental standards. It is performed by recognized agencies that assess various aspects such as structural integrity, electrical systems, and emissions.
RV certification requirements, like a certificate of electrical compliance for an RV, vary by country or state, and manufacturers must comply with the regulations before selling an RV. The effectiveness of RV certification lasts, as the vehicle meets the required standards and does not undergo major modifications.
RV certifications remain valid for the vehicle’s life unless changes affect compliance once an RV is certified. New certifications are required if the RV undergoes major modifications or the car is re-certified after a few years. RV owners must check the validity and expiration of RV certification to ensure the vehicle remains compliant with safety and regulatory standards.

How to Get an RV Certification?
To get an RV Certification, follow the five steps below.
- Enroll in an Accredited RV Training Program. Begin by enrolling in a recognized RV training program like the RV Technical Institute offered. The programs provide comprehensive education on RV systems and maintenance. Completing such a program equips owners with the required skills and knowledge for certification.
- Complete Required Coursework and Practical Training. Engage in theoretical coursework and hands-on practical training. Practical experience is essential for developing the skills needed to pass certification exams.
- Pass Certification Examinations. Candidates RV owners must pass written and practical exams to demonstrate competency after training. The exams assess knowledge and practical skills in RV maintenance and repair.
- Apply for Certification. Apply to certifying the RV Technician Association of America (RVTAA). The application process requires proof of completed training and exam results. RV owners receive their official RV certification upon approval.
- Maintain Certification Through Continuing Education. Engage in ongoing education and training to keep the certification valid. Continuing education is a requirement for maintaining certification status.

What Safety Features are Required for RVs?

The safety features that are required for RVs are listed below.
- Fire Extinguisher: A fire extinguisher is mandatory in every RV for safety in a fire. It must be easily accessible and placed near cooking or heating areas. Proper maintenance ensures the fire extinguishers are ready to use in emergencies.
- Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Carbon monoxide detectors are required to detect dangerous gas levels from faulty appliances or engine systems. The detectors must be placed near sleeping areas for maximum protection.
- Smoke Detectors: Smoke detectors are essential to alert RV occupants in case of a fire. Smoke detectors are installed in or near living and sleeping areas. Upgrading to a smart smoke detection system provides more accurate alerts for safety.
- Brakes: Brakes are required for all RVs, and proper braking systems are required to ensure safe stopping. The brakes must be regularly checked for functionality and wear.
- Seatbelts: Seatbelts are required for all passengers in moving RVs, including the sleeping areas. The seatbelts must be securely attached to the vehicle’s frame. Seatbelt compliance helps prevent injury in sudden stops or accidents.
- Emergency Exits: Emergency exits allow quick evacuation in case of an emergency. RVs must have marked exits that are easy to open from inside and outside, and the exits must always be clear.
- Wheel Chocks: Wheel chocks are required to prevent RVs from rolling when parked. Wheel chocks are essential on inclines or uneven terrain. Proper use of wheelchocks enhances parking stability and safety.
- Backup Cameras: Backup cameras provide an extra layer of safety when reversing. Cameras help prevent collisions with obstacles or pedestrians. Installing high-quality backup cameras for RV upgrades ensures a safer driving experience.
- Propane Leak Detector: A propane leak detector helps identify gas leaks from propane tanks and appliances. Regular checks and replacements of detectors are essential for safe RV operation.
- Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS): A TPMS alerts owners to unsafe tire conditions, such as low tire pressure or overheating. Proper tire maintenance is essential for safe driving. A well-functioning TPMS reduces the risk of tire-related accidents.
What are the Insurance Requirements for RVs?
The Insurance Requirements for RVs are set by state laws, with most states requiring a minimum liability coverage for RV owners. The minimum liability coverage includes bodily injury and property damage liability to protect others in the event of an accident caused by the RV owner.
States require higher limits based on the type of RV and its use. The liability coverage of the towing vehicle extends to the trailer for towable RVs like travel trailers. Additional coverage options, like collision, comprehensive, and personal belonging coverage, enhance protection.
Collision coverage helps pay for repairs or replacement if the RV is damaged in an accident, regardless of fault. Comprehensive coverage protects against non-collision incidents like theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. Personal belongings coverage covers items inside the RV, such as electronics and clothing, in case of loss or damage. Owners opt for the extra RV Insurance for added peace of mind while traveling.

How do Zoning Laws Affect RV Living?
Zoning laws affect RV living through municipal regulations on residential property use and occupancy standards, and local governments enforce strict parking limits for RVs on driveways or private properties. Homeowners risk fines of up to $1,000 for unauthorized long-term RV parking, while municipal codes restrict full-time RV living to designated parks or campgrounds.
Residential zoning ordinances set maximum RV parking between 24 to 72 hours on private property, and property owners must follow minimum setback distances between parked RVs and property lines. Special permits allow temporary RV living under specific conditions set by local authorities, and emergency declarations make RV occupancy possible in home renovations or natural disasters.
Medical hardship permits family caregivers to live in an RV, while agricultural zones allow seasonal RV housing for farmworkers. Rural properties outside municipal boundaries have fewer RV living restrictions, and designated RV-friendly communities offer zoning exemptions through proper permits. Mobile home park zoning allows permanent RV placement with utility connections while providing a stable living option.

What Rules Apply to RV Modifications?
The rules apply to RV modifications, depending on location and the type of change being made. Structural changes like altering the frame, extending the body, or adding extra rooms require permits and must meet safety regulations. Engine upgrades must follow emissions laws, and some states require inspections before the RV is legally allowed on the road.
Electrical and plumbing modifications must comply with local building codes to prevent hazards. DIY modifications without proper approval risk violating safety laws, which result in fines or the RV being unfit to use. Unauthorized modifications void manufacturer warranties if changes affect the engine, electrical system, or structural integrity. Safety and emissions compliance are required to avoid legal issues and maintain roadworthiness.
Modifications that increase weight beyond the vehicle’s capacity lead to mechanical failures and reduced stability. Checking with local authorities or professionals before making modifications helps ensure all upgrades follow legal and safety requirements.

What are Common Campground Rules?
The Common Campground Rules are listed below.
- Check-in and Check-out Times: Campgrounds set specific check-in and check-out times to manage guest flow. Owners must adhere to the times between 1 PM and 3 PM for check-in and by noon for check-out.
- Quiet Hours: Quiet hours ensure a peaceful environment for all campers from 10 PM to 7 AM, restricting loud noises and disturbances.
- Generator Restrictions: Campgrounds restrict generator use to certain hours to avoid disturbing others. Generators are allowed from 8 AM to 8 PM, but times vary by location.
- Pet Policies: Campgrounds allow pets but require them to be kept on a leash. Owners must clean up after pets and follow campground-specific pet guidelines.
- Campfire Rules: Campgrounds allow campfires in designated fire pits. Open flames are restricted in dry conditions to prevent wildfires.
- Waste Disposal: Proper waste disposal is mandatory at all campgrounds. RV owners must dispose of trash and sewage in designated bins or dump stations.
- RV Hookups: Campsites offer hookups for water, electricity, and sewage. Campers must connect their RV Campground to the systems as needed and follow the campground’s rules for use.
- Vehicle Parking: Campgrounds require parking in designated areas near the campsite. Extra vehicles are subject to additional charges or require parking in a separate lot.
- Noise and Music Policies: Campgrounds restrict loud music or noise to avoid disturbing other campers. Campers must use headphones or keep music at a low volume.
- Amenity Usage: Pools, showers, and recreational areas are available but have specific hours or occupancy limits. RV owners must follow posted guidelines and respect shared spaces.

Is Full-Time RV Living Legal?
Yes, full-time RV living is legal across different states. RV residents establish legal residency addresses through mail forwarding services in RV-friendly states like Texas, Florida, or South Dakota. Local zoning laws restrict permanent RV parking in residential areas or private property. Homeowner associations enforce strict rules against extended RV occupancy in neighborhoods.
State vehicle registration requirements mandate periodic renewal for full-time RV owners. Federal campgrounds limit continuous stays between 14 to 30 days per location, and private RV parks welcome extended stays through long-term lease agreements. Full-time RV residents maintain legal compliance through proper documentation and established residency. Vehicle insurance policies require permanent address verification for coverage, while State driver’s licenses need physical addresses for renewal processes.
Tax documents for filing purposes depend on declared residency states. Bank accounts link to permanent mailing addresses for financial services. Healthcare plans connect to primary residence locations for coverage areas. Voter registration aligns with the chosen RV Living requirements for participation, and Social Security benefits continue through designated permanent addresses for full-time RV owners.

Are RV Inspections Required?
Yes, RV Inspections are required in states based on vehicle weight classifications and usage categories. Annual safety inspections check brake systems, lights, tires, and structural integrity for RVs exceeding 10,000 pounds. Texas mandates yearly RV safety inspections on steering components, suspension parts, and exhaust systems.
California requires biennial smog checks for gas-powered RVs manufactured after 1976. Florida enforces annual LP gas system inspections for motorhomes with propane appliances. New York state demands comprehensive safety checks, including frame condition, wheel alignment, and windshield integrity.
Maine requires annual safety inspections for all motorized RVs, regardless of size or class. Pennsylvania enforces semi-annual brake inspections for RVs weighing over 17,000 pounds. Hawaii mandates yearly reconstruction inspections for modified or upgraded RVs.
Oregon implements emissions testing for RVs in metropolitan counties, while Maryland requires safety certifications before title transfers between owners. Utah enforces special transportation permits for oversized RVs exceeding standard dimensions. Nevada mandates equipment inspections for commercial RV rentals operating within state lines.

What are the Rules for Cross-Border RV Travel?
The Rules for Cross-Border RV Travel require valid passports for all RV owners entering Canada or Mexico, and the U.S. Department of State mandates that the original vehicle registration documents be in the owner’s name. Border officials demand proof of RV insurance coverage valid in foreign countries, while every adult passenger needs a government-issued photo ID for customs inspections.
RV owners present vehicle title or lien holder documentation at border crossings, and pet travelers require current vaccination records from licensed veterinarians. Customs declarations list all items brought across international borders and must be presented at inspection points. Mexican border crossings require temporary vehicle import permits, which must be purchased online before arrival, while Canadian entry needs to complete CBP-4455 customs forms listing RV modifications or upgrades.
Mexican authorities collect deposits based on RV value through Banjercito processing, and Canadian borders restrict the entry of firearms, certain foods, and alcohol quantities. Mexican insurance policies are mandatory for all RV travelers, and Canadian provinces enforce strict length and weight restrictions on RVs. Border agents inspect RVs for compliance with emissions standards, and entry is denied for missing or incomplete travel documentation.

What are the Penalties for Violating RV Laws?
The penalties for violating RV laws lead to heavy fines and legal trouble in the States. Federal rules set penalties between $500 and $5,000 for serious transportation violations, and illegal parking results in towing fees from $150 to $500 per incident. Overweight RVs face penalties up to $2,500 per axle, and repeated violations or huge safety issues cause registration suspension.
Commercial RV operators face stricter penalties under business vehicle rules, while failure to follow regulations leads to further legal action and financial loss. State laws focus on specific RV operation rules, and highway patrol units conduct required weight station checks for all RVs.
Registration gets revoked after three moving violations in twelve months, while California, Texas, and Florida impose stricter transportation rules with higher fines. Local laws add extra location-based restrictions, and unsafe towing leads to immediate impoundment and required safety inspections.
